Step 1: Static Coseismic Slip#
Features
Triangular cells
pylith.meshio.MeshIOPetsc
pylith.problems.TimeDependent
pylith.materials.Elasticity
pylith.materials.IsotropicLinearElasticity
pylith.faults.FaultCohesiveKin
pylith.faults.KinSrcStep
field split preconditioner
Schur complement preconditioner
pylith.bc.DirichletTimeDependent
spatialdata.spatialdb.UniformDB
pylith.meshio.OutputSolnBoundary
pylith.meshio.DataWriterHDF5
Static simulation
Simulation parameters#
This example involves a static simulation that solves for the deformation from prescribed coseismic slip on the fault.
Fig. 54 shows the boundary conditions on the domain.
The parameters specific to this example are in step01_slip.cfg.
Fig. 54 Boundary conditions for static coseismic slip. We set the x and y displacement to zero on the +x and -x boundaries and prescribe 2 meters of right-lateral slip.#
[pylithapp.problem.interfaces.fault.eq_ruptures.rupture]
db_auxiliary_field = spatialdata.spatialdb.UniformDB
db_auxiliary_field.description = Fault rupture auxiliary field spatial database
db_auxiliary_field.values = [initiation_time, final_slip_left_lateral, final_slip_opening]
db_auxiliary_field.data = [0.0*s, -2.0*m, 0.0*m]
Running the simulation#
$ pylith step01_slip.cfg
# The output should look something like the following.
>> /software/unix/py39-venv/pylith-debug/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pylith/meshio/MeshIOObj.py:44:read
-- meshiopetsc(info)
-- Reading finite-element mesh
>> /src/cig/pylith/libsrc/pylith/meshio/MeshIO.cc:94:void pylith::meshio::MeshIO::read(topology::Mesh *)
-- meshiopetsc(info)
-- Component 'reader': Domain bounding box:
(-50000, 50000)
(-75000, 75000)
>> /software/unix/py39-venv/pylith-debug/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pylith/faults/FaultCohesiveKin.py:93:preinitialize
-- faultcohesivekin(info)
-- Pre-initializing fault 'fault'.
>> /software/unix/py39-venv/pylith-debug/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pylith/problems/Problem.py:116:preinitialize
-- timedependent(info)
-- Performing minimal initialization before verifying configuration.
>> /software/unix/py39-venv/pylith-debug/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pylith/problems/Solution.py:44:preinitialize
-- solution(info)
-- Performing minimal initialization of solution.
>> /software/unix/py39-venv/pylith-debug/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pylith/materials/RheologyElasticity.py:41:preinitialize
-- isotropiclinearelasticity(info)
-- Performing minimal initialization of elasticity rheology 'bulk_rheology'.
>> /software/unix/py39-venv/pylith-debug/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pylith/materials/RheologyElasticity.py:41:preinitialize
-- isotropiclinearelasticity(info)
-- Performing minimal initialization of elasticity rheology 'bulk_rheology'.
>> /software/unix/py39-venv/pylith-debug/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pylith/bc/DirichletTimeDependent.py:92:preinitialize
-- dirichlettimedependent(info)
-- Performing minimal initialization of time-dependent Dirichlet boundary condition 'bc_xneg'.
>> /software/unix/py39-venv/pylith-debug/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pylith/bc/DirichletTimeDependent.py:92:preinitialize
-- dirichlettimedependent(info)
-- Performing minimal initialization of time-dependent Dirichlet boundary condition 'bc_xpos'.
>> /software/unix/py39-venv/pylith-debug/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pylith/faults/FaultCohesiveKin.py:93:preinitialize
-- faultcohesivekin(info)
-- Pre-initializing fault 'fault'.
>> /software/unix/py39-venv/pylith-debug/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pylith/problems/Problem.py:175:verifyConfiguration
-- timedependent(info)
-- Verifying compatibility of problem configuration.
>> /software/unix/py39-venv/pylith-debug/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pylith/problems/Problem.py:221:_printInfo
-- timedependent(info)
-- Scales for nondimensionalization:
Length scale: 1000*m
Time scale: 3.15576e+09*s
Pressure scale: 3e+10*m**-1*kg*s**-2
Density scale: 2.98765e+23*m**-3*kg
Temperature scale: 1*K
>> /software/unix/py39-venv/pylith-debug/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pylith/problems/Problem.py:186:initialize
-- timedependent(info)
-- Initializing timedependent problem with quasistatic formulation.
>> /src/cig/pylith/libsrc/pylith/utils/PetscOptions.cc:235:static void pylith::utils::_PetscOptions::write(pythia::journal::info_t &, const char *, const pylith::utils::PetscOptions &)
-- petscoptions(info)
-- Setting PETSc options:
fieldsplit_displacement_ksp_type = preonly
fieldsplit_displacement_pc_type = lu
fieldsplit_lagrange_multiplier_fault_ksp_type = preonly
fieldsplit_lagrange_multiplier_fault_pc_type = lu
ksp_atol = 1.0e-12
ksp_converged_reason = true
ksp_error_if_not_converged = true
ksp_rtol = 1.0e-12
pc_fieldsplit_schur_factorization_type = lower
pc_fieldsplit_schur_precondition = selfp
pc_fieldsplit_schur_scale = 1.0
pc_fieldsplit_type = schur
pc_type = fieldsplit
pc_use_amat = true
snes_atol = 1.0e-9
snes_converged_reason = true
snes_error_if_not_converged = true
snes_monitor = true
snes_rtol = 1.0e-12
ts_error_if_step_fails = true
ts_monitor = true
ts_type = beuler
>> /software/unix/py39-venv/pylith-debug/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pylith/problems/TimeDependent.py:139:run
-- timedependent(info)
-- Solving problem.
0 TS dt 0.01 time 0.
0 SNES Function norm 4.895713226482e-02
Linear solve converged due to CONVERGED_ATOL iterations 35
1 SNES Function norm 2.540698951426e-12
Nonlinear solve converged due to CONVERGED_FNORM_ABS iterations 1
1 TS dt 0.01 time 0.01
>> /software/unix/py39-venv/pylith-debug/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pylith/problems/Problem.py:201:finalize
-- timedependent(info)
-- Finalizing problem.
At the beginning of the output written to the terminal, we see that PyLith is reading the mesh using the MeshIOPetsc reader and that it found the domain to extend from -50,000 m to +50,000 m in the x direction and from -75,000 m to +75,000 m in the y direction.
The scales for nondimensionalization remain the default values for a quasistatic problem.
PyLith detects the presence of a fault based on the Lagrange multiplier for the fault in the solution field and selects appropriate preconditioning options as discussed in PETSc Options.
At the end of the output written to the terminal, we see that the solver advanced the solution one time step (static simulation).
The linear solve converged after 35 iterations and the norm of the residual met the absolute convergence tolerance (ksp_atol) .
The nonlinear solve converged in 1 iteration, which we expect because this is a linear problem, and the residual met the absolute convergence tolerance (snes_atol).
Visualizing the results#
The output directory contains the simulation output.
Each “observer” writes its own set of files, so the solution over the domain is in one set of files, the boundary condition information is in another set of files, and the material information is in yet another set of files.
The HDF5 (.h5) files contain the mesh geometry and topology information along with the solution fields.
The Xdmf (.xmf) files contain metadata that allow visualization tools like ParaView to know where to find the information in the HDF5 files.
To visualize the data using ParaView or Visit, load the Xdmf files.
In Fig. 55 we use ParaView to visualize the y displacement field using the viz/plot_dispwarp.py Python script.
First, we start ParaView from the examples/strikeslip-2d directory.
$ PATH_TO_PARAVIEW/paraview
# For macOS, it will be something like
$ /Applications/ParaView-5.10.1.app/Contents/MacOS/paraview
Next we run the viz/plot_dispwarp.py Python script as described in ParaView Python Scripts.
For Step 1 we do not need to change any of the default values.
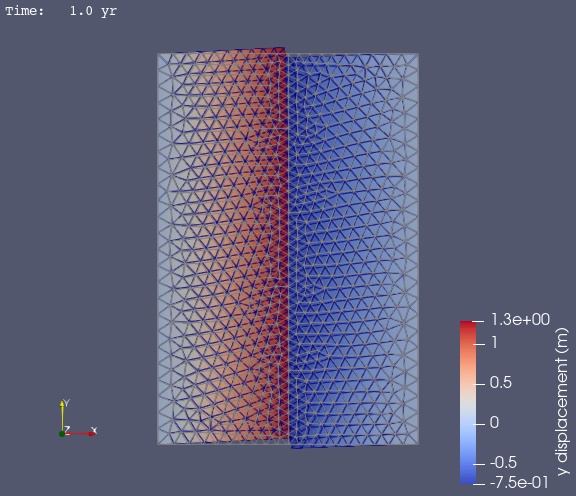
Fig. 55 Solution for Step 1. The colors of the shaded surface indicate the magnitude of the y displacement, and the deformation is exaggerated by a factor of 1000. The undeformed configuration is show by the gray wireframe. The contrast in material properties across the faults causes the asymmetry in the y displacement field.#
Step 1 with Cubit Mesh#
Using the Cubit mesh rather than the Gmsh mesh involves two changes:
Use the
MeshIOCubitreader instead of theMeshIOPetscreader and change the filename of the mesh file.Set the
label_valueto 1 for boundary conditions and faults.
We must override the nondefaultlabel_valuesettings inpylithapp.cfgthat were appropriate for our Gmsh reader but are incorrect for the Cubit reader.
The file step01_slip_cubit.cfg provides these changes and updates the names for output.
$ pylith step01_slip_cubit.cfg
# The output should look something like the following.
>> /software/unix/py39-venv/pylith-debug/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pylith/meshio/MeshIOObj.py:44:read
-- meshiocubit(info)
-- Reading finite-element mesh
>> /src/cig/pylith/libsrc/pylith/meshio/MeshIOCubit.cc:157:void pylith::meshio::MeshIOCubit::_readVertices(pylith::meshio::ExodusII &, pylith::scalar_array *, int *, int *) const
-- meshiocubit(info)
-- Component 'reader': Reading 682 vertices.
>> /src/cig/pylith/libsrc/pylith/meshio/MeshIOCubit.cc:217:void pylith::meshio::MeshIOCubit::_readCells(pylith::meshio::ExodusII &, pylith::int_array *, pylith::int_array *, int *, int *) const
-- meshiocubit(info)
-- Component 'reader': Reading 1276 cells in 2 blocks.
>> /src/cig/pylith/libsrc/pylith/meshio/MeshIOCubit.cc:279:void pylith::meshio::MeshIOCubit::_readGroups(pylith::meshio::ExodusII &)
-- meshiocubit(info)
-- Component 'reader': Found 5 node sets.
>> /src/cig/pylith/libsrc/pylith/meshio/MeshIOCubit.cc:305:void pylith::meshio::MeshIOCubit::_readGroups(pylith::meshio::ExodusII &)
-- meshiocubit(info)
-- Component 'reader': Reading node set 'fault' with id 10 containing 39 nodes.
>> /src/cig/pylith/libsrc/pylith/meshio/MeshIOCubit.cc:305:void pylith::meshio::MeshIOCubit::_readGroups(pylith::meshio::ExodusII &)
-- meshiocubit(info)
-- Component 'reader': Reading node set 'boundary_xpos' with id 21 containing 24 nodes.
>> /src/cig/pylith/libsrc/pylith/meshio/MeshIOCubit.cc:305:void pylith::meshio::MeshIOCubit::_readGroups(pylith::meshio::ExodusII &)
-- meshiocubit(info)
-- Component 'reader': Reading node set 'boundary_xneg' with id 22 containing 24 nodes.
>> /src/cig/pylith/libsrc/pylith/meshio/MeshIOCubit.cc:305:void pylith::meshio::MeshIOCubit::_readGroups(pylith::meshio::ExodusII &)
-- meshiocubit(info)
-- Component 'reader': Reading node set 'boundary_ypos' with id 23 containing 21 nodes.
>> /src/cig/pylith/libsrc/pylith/meshio/MeshIOCubit.cc:305:void pylith::meshio::MeshIOCubit::_readGroups(pylith::meshio::ExodusII &)
-- meshiocubit(info)
-- Component 'reader': Reading node set 'boundary_yneg' with id 24 containing 21 nodes.
>> /src/cig/pylith/libsrc/pylith/meshio/MeshIO.cc:94:void pylith::meshio::MeshIO::read(topology::Mesh *)
-- meshiocubit(info)
-- Component 'reader': Domain bounding box:
(-50000, 50000)
(-75000, 75000)
# -- many lines omitted --
>> /software/unix/py39-venv/pylith-debug/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pylith/problems/TimeDependent.py:139:run
-- timedependent(info)
-- Solving problem.
0 TS dt 0.01 time 0.
0 SNES Function norm 4.834519229177e-02
Linear solve converged due to CONVERGED_ATOL iterations 35
1 SNES Function norm 2.664525811959e-12
Nonlinear solve converged due to CONVERGED_FNORM_ABS iterations 1
1 TS dt 0.01 time 0.01
>> /software/unix/py39-venv/pylith-debug/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pylith/problems/Problem.py:201:finalize
-- timedependent(info)
-- Finalizing problem.
The MeshIOCubit reader includes diagnostic information in the journal output related to the sizes of the nodesets and material blocks.

