Gmsh Mesh#
Geometry#
We create the geometry directly from the box primitive provided by the OpenCascade geometry engine in Gmsh.
Meshing using Python Script#
We use the Python script generate_gmsh.py to create the geometry and generate the mesh.
The script makes use of the gmsh_utils.GenerateMesh class (discussed in gmsh_utils), which provides the command line arguments and boilerplate methods.
In our generate_gmsh.py Python script, we create a class App that implements the functionality missing in gmsh_utils.GenerateMesh.
We must implement the create_geometry(), mark(), and generate_mesh() methods that are abstract in the GenerateMesh base class.
We use the Gmsh MeshSize options to define a uniform discretization size of 3 km.
# Generate a mesh with hexahedral cells and save it to `mesh_hex.msh` (default filename).
$ ./generate_gmsh.py --write
# Save as above but start the Gmsh graphical interface after saving the mesh.
$ ./generate_gmsh.py --write --gui
# Create only the geometry and start the Gmsh graphical interface.
$ ./generate_gmsh.py --geometry --gui
# Show available command line arguments.
$ ./generate_gmsh.py --help
By default the Python script will generate a finite-element mesh with hexahedral cells and save it to the file mesh_hex.msh.
You can view the mesh using Gmsh either by using the --gui command line argument when you generate the mesh or running Gmsh from the command line and opening the file.
gmsh -open mesh_hex.msh
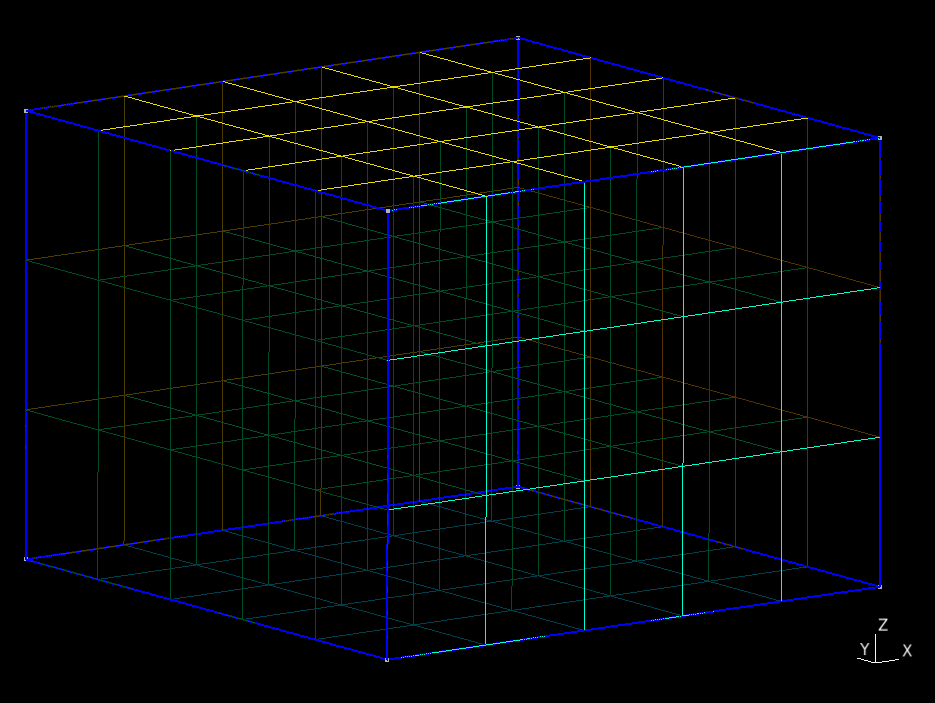
Fig. 36 Finite-element mesh with hexahedral cells generated by Gmsh.#
